Incretin-based Therapies - Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
Incretin-based Therapies FAQ
What are incretin based therapies?
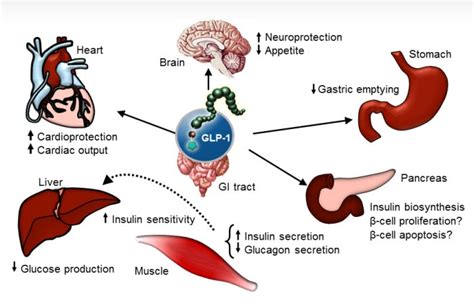
Incretin‐based therapies have emerged that make use of the incretin system, which comprises the incretin hormones glucagon‐like peptide‐1 (GLP‐1) and glucose‐dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) that stimulate the release of insulin from pancreatic β cells at elevated glucose concentrations 4.
What are the different types of incretin therapy?
There are two classes of incretin therapies: dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 (DPP‐4) inhibitors, which prevent the proteolytic breakdown and inactivation of GLP‐1 and GLP‐1 receptor agonists (GLP‐1RAs), which provide supraphysiological concentrations of ligands that stimulate the GLP‐1R 8.
Can incretin be used in type 2 diabetes?
These agents offer some potential advantages over previous antidiabetes drugs and have been approved for use in type 2 diabetes. There are two broad classes of incretin-related therapies: dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (sitagliptin and saxagliptin) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (exenatide and liraglutide).
What are incretin-based drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Incretin-based drugs, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, are now routinely used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Who should take incretin based therapies?
Incretin-based drugs are most often used by people with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity to manage blood sugar levels and body weight. Incretin-based therapies can be taken alone, or with metformin or other diabetes medications. Who should not take incretin-based therapies? There have been very few studies conducted in type 1 diabetes.
How do incretin-based therapies work?
Incretin-based therapies work by copying (“mimicking”) the actions of natural incretin hormones, which help lower blood sugar after eating. For this reason, incretin-based drugs are sometimes called incretin mimetics. Incretin-based therapies act in the following ways: Stimulating insulin secretion, which then allows cells to take up glucose.
Can incretin therapy improve patient care?
Physicians can therefore use incretin therapies to manage patient care effectively and provide tailored treatment regimens that may promote increased adherence to therapy, improve outcomes and potentially slow down disease progression. The full potential of the incretin therapies, however, may not yet have been appreciated.
Incretin-based Therapies References
If you want to know more about Incretin-based Therapies, consider exploring links below:
What Is Incretin-based Therapies
- https://dtc.ucsf.edu/types-of-diabetes/type2/treatment-of-type-2-diabetes/medications-and-therapies/type-2-non-insulin-therapies/incretin-based-treatments/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2809297/
- https://diabetesjournals.org/spectrum/article/24/1/26/32481/Incretin-Related-Therapies-in-Type-2-Diabetes-A
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25456646/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nrendo.2009.48
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.2147/tcrm.s4975
Incretin-based Therapies Information
Explore Related Topics
Diabetes Costs Getting You Down? Let's Find Solutions!
Collaborate on creative ways to offset the financial burden of diabetes