Learn About Carbohydrate Metabolism for Better Health
Carbohydrate Metabolism FAQ
What is carbohydrate metabolism?
Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms . Carbohydrates are central to many essential metabolic pathways.
What are the different types of carbohydrate metabolism?
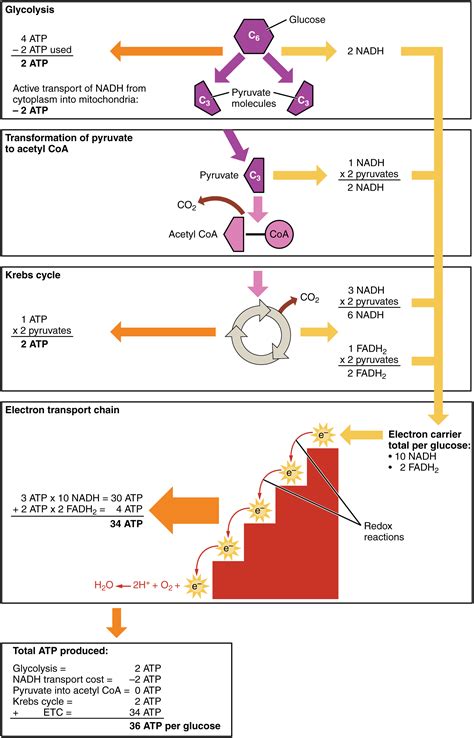
Overview of carbohydrate metabolism. Simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, or galactose, have different points of entry into glycolysis. A process referred to as gluconeogenesis can also generate glucose. Complex carbohydrates such as glycogen can also enter glycolysis.
What are the pathways of carbohydrate metabolism?
The pathways of carbohydrate metabolism conform to the principles of thermodynamics (Chapter 10 ). Each pathway is overall exergonic. For example, as calculated from thermodynamic data, the degradation of glucose to two lactate molecules proceeds with the release of free energy according to the equation:
What is the role of carbohydrates in the human body?
Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism, and help with fermentation. The digestive tract begins to break down carbohydrates into glucose, which is used for energy upon consumption.
Carbohydrate Metabolism References
If you want to know more about Carbohydrate Metabolism, consider exploring links below:
What Is Carbohydrate Metabolism
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/Lumen_Learning/Anatomy_and_Physiology_II_(Lumen)/10%3A_Module_8-_Metabolism_and_Nutrition/10.03%3A_Carbohydrate_Metabolism
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbohydrate_metabolism
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7778149/
- https://open.oregonstate.education/aandp/chapter/24-2-carbohydrate-metabolism/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/carbohydrate-metabolism
- https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?sectionid=185844537
Carbohydrate Metabolism Information
- https://med.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Anatomy_and_Physiology/Anatomy_and_Physiology_1e_(OpenStax)/Unit_5%3A_Energy_Maintenance_and_Environmental_Exchange/24%3A_Metabolism_and_Nutrition/24.02%3A_Carbohydrate_Metabolism
- https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/humananatomyandphysiology/chapter/24-2-carbohydrate-metabolism/
Explore Related Topics
Chromium Supplements: Are They Effective for Blood Sugar Control?
Analyze the impact of chromium supplementation on blood glucose levels.