Combining DPP-4 Inhibitors with Other Medications for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Gain insights into the benefits and considerations of using DPP-4 inhibitors in combination therapy for diabetes.
Combining DPP-4 Inhibitors with Other Medications for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Posted by Jane Cox, reviewed by Lee Cheng | 2024-Mar-24
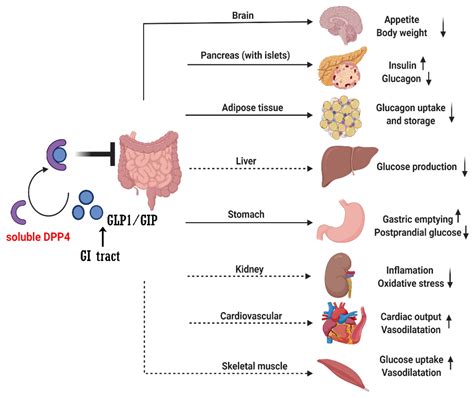
Diabetes is a complex condition that often requires a multifaceted approach to management. In recent years, the introduction of DPP-4 inhibitors has provided healthcare professionals with a valuable tool in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. These medications work by inhibiting the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), which in turn increases the levels of incretin hormones like GLP-1 and GIP. This can lead to improved blood glucose control and other beneficial effects.
"DPP-4 inhibitors have emerged as an important class of medications for the management of type 2 diabetes, offering a unique mechanism of action that can complement other therapies."
However, in many cases, the use of DPP-4 inhibitors alone may not be sufficient to achieve optimal glycemic control. This is where combination therapy comes into play, with healthcare providers often opting to prescribe DPP-4 inhibitors in conjunction with other diabetes medications.
One of the key advantages of combining DPP-4 inhibitors with other medications is the potential for enhanced glycemic control. By targeting multiple pathways involved in glucose regulation, this approach can lead to more effective management of blood sugar levels. Additionally, the use of combination therapy may allow for lower doses of individual medications, potentially reducing the risk of side effects.
"Combining DPP-4 inhibitors with other diabetes medications can provide a synergistic effect, leading to improved glycemic control and potentially reducing the risk of side effects."
Another important consideration is the impact of combination therapy on cardiovascular outcomes. Several studies have suggested that the use of DPP-4 inhibitors, particularly when combined with other medications, may have a positive effect on cardiovascular health. This can be particularly relevant for individuals with type 2 diabetes, who often have an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
"Emerging evidence suggests that the use of DPP-4 inhibitors in combination with other medications may have favorable effects on cardiovascular outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes."
When it comes to the specific combinations of DPP-4 inhibitors and other diabetes medications, healthcare providers may consider a range of options. Common combinations include DPP-4 inhibitors with metformin, sulfonylureas, insulin, GLP-1 agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors. The choice of combination will depend on factors such as the individual's response to treatment, the presence of comorbidities, and the potential for drug interactions.
"Healthcare providers may consider a variety of combination therapies involving DPP-4 inhibitors, including with metformin, sulfonylureas, insulin, GLP-1 agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors, depending on the individual's needs and response to treatment."
As with any medication regimen, the use of DPP-4 inhibitors in combination with other diabetes medications requires close monitoring and careful consideration of potential side effects and interactions. Healthcare providers will typically work closely with their patients to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the prescribed treatment plan.
In conclusion, the combination of DPP-4 inhibitors with other diabetes medications can offer a valuable approach to managing this complex condition. By leveraging the unique mechanisms of action of these therapies, healthcare providers can strive to achieve improved glycemic control, potentially reduced side effects, and potentially favorable cardiovascular outcomes. As always, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual's needs.
What are your experiences with the use of DPP-4 inhibitors in combination with other diabetes medications? We'd love to hear your thoughts and perspectives on this important topic.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
Is Combining Insulin with Oral Medications Effective for Diabetes Management?
Delve into the benefits and challenges of using a combination of insulin and oral medications for diabetes.
Exploring the Role of Metformin in Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Investigate the impact of metformin when used in combination therapy for diabetes management.
Are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists A Game-Changer in Combination Therapy for Diabetes?
Discuss the effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists as part of combination therapy for diabetes.
Combination Therapy: Balancing Insulin and Sulfonylureas for Diabetes Control
Balance the use of insulin and sulfonylureas in combination therapy for optimal diabetes control.
SGLT2 Inhibitors in Combination Therapy: An Emerging Trend in Diabetes Treatment?
Evaluate the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in the evolving landscape of combination therapy for diabetes.
Mixing Biguanides with Other Medications: Exploring Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Examine the implications of combining biguanides with other medications for diabetes treatment.
Beyond Monotherapy: The Impact of Combination Therapy in Diabetes Care
Dive into the significance of transitioning from monotherapy to combination therapy in diabetes care.
Combination Therapy: Harnessing the Power of Multiple Agents for Diabetes Control
Uncover the synergistic effects of utilizing multiple agents in combination therapy for diabetes control.
Patient Perspectives on Combination Therapy: Shaping Diabetes Treatment Strategies
Explore the patient-centric approach to integrating combination therapy into diabetes treatment strategies.