Exploring the Role of Metformin in Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Investigate the impact of metformin when used in combination therapy for diabetes management.
Exploring the Role of Metformin in Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Posted by Jane Cox, reviewed by Lee Cheng | 2024-Mar-11
Diabetes is a prevalent and complex metabolic disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. As healthcare professionals continue to explore effective treatment strategies, the use of combination therapy, where multiple medications are prescribed together, has gained significant attention. One such combination that has garnered substantial interest is the incorporation of metformin, a widely-used first-line medication, into combination regimens for diabetes management.
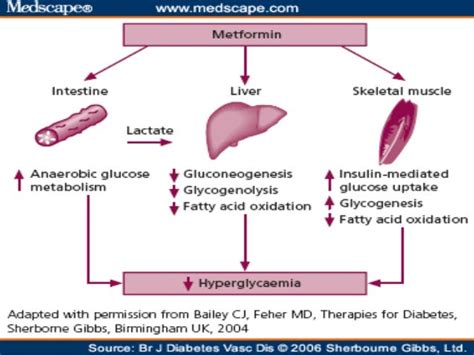
Metformin, a biguanide class medication, has long been recognized for its ability to lower blood glucose levels by reducing hepatic glucose production and enhancing insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. However, its potential extends beyond its standalone efficacy, as researchers have been investigating the benefits of using metformin in combination with other antidiabetic medications.
"Metformin has been a mainstay in diabetes treatment for decades, but its true potential may lie in its ability to synergize with other therapies," explains Dr. Emma Walters, a leading endocrinologist.
One of the key advantages of using metformin in combination therapy is its ability to potentially enhance the efficacy of other antidiabetic drugs. When used in combination with medications such as sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, or GLP-1 agonists, metformin has been shown to provide additive or even synergistic effects in improving glycemic control.
"By targeting different pathways in the body, metformin and other diabetes medications can work together to achieve better blood glucose regulation and improved overall management of the disease," says Dr. Walters.
Additionally, metformin's favorable safety profile and low risk of hypoglycemia make it an attractive option for inclusion in combination regimens. This is particularly relevant when considering the importance of minimizing the risk of adverse events, especially in individuals with comorbidities or advanced stages of the disease.
Interestingly, some research has also explored the potential of metformin in combination with insulin therapy. By improving insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance, metformin may help to optimize the effectiveness of exogenous insulin administration, potentially leading to better glycemic control and a reduced risk of insulin-related complications.
"The synergistic effects of metformin and insulin can be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy," explains Dr. Walters. "By enhancing insulin sensitivity, metformin can help to minimize the insulin dosage required, which can have important implications for weight management and overall metabolic health."
As the field of diabetes management continues to evolve, the role of metformin in combination therapy is likely to remain a topic of active research and clinical exploration. Healthcare professionals will need to carefully consider the specific needs and characteristics of each patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of various combination regimens to optimize the management of this complex and multifaceted condition.
What are your thoughts on the use of metformin in combination therapy for diabetes management? Do you have personal experiences or insights to share? We encourage you to engage in the discussion and share your perspectives on this important topic.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
Is Combining Insulin with Oral Medications Effective for Diabetes Management?
Delve into the benefits and challenges of using a combination of insulin and oral medications for diabetes.
Are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists A Game-Changer in Combination Therapy for Diabetes?
Discuss the effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists as part of combination therapy for diabetes.
Combination Therapy: Balancing Insulin and Sulfonylureas for Diabetes Control
Balance the use of insulin and sulfonylureas in combination therapy for optimal diabetes control.
SGLT2 Inhibitors in Combination Therapy: An Emerging Trend in Diabetes Treatment?
Evaluate the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in the evolving landscape of combination therapy for diabetes.
Combining DPP-4 Inhibitors with Other Medications for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Gain insights into the benefits and considerations of using DPP-4 inhibitors in combination therapy for diabetes.
Mixing Biguanides with Other Medications: Exploring Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Examine the implications of combining biguanides with other medications for diabetes treatment.
Beyond Monotherapy: The Impact of Combination Therapy in Diabetes Care
Dive into the significance of transitioning from monotherapy to combination therapy in diabetes care.
Combination Therapy: Harnessing the Power of Multiple Agents for Diabetes Control
Uncover the synergistic effects of utilizing multiple agents in combination therapy for diabetes control.
Patient Perspectives on Combination Therapy: Shaping Diabetes Treatment Strategies
Explore the patient-centric approach to integrating combination therapy into diabetes treatment strategies.