SGLT2 Inhibitors in Combination Therapy: An Emerging Trend in Diabetes Treatment?
Evaluate the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in the evolving landscape of combination therapy for diabetes.
SGLT2 Inhibitors in Combination Therapy: An Emerging Trend in Diabetes Treatment?
Posted by Jane Cox, reviewed by Lee Cheng | 2024-Mar-21
As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, healthcare professionals are constantly seeking innovative ways to manage this chronic condition more effectively. One such area of exploration is the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy, which has been gaining significant traction in recent years.
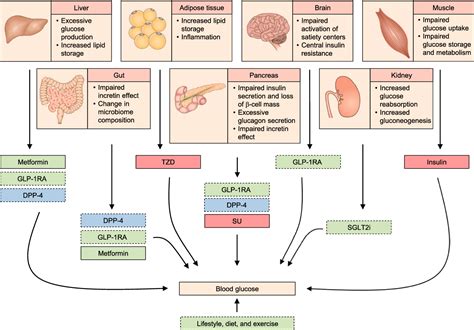
SGLT2 inhibitors, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, are a class of medications that work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased urinary glucose excretion. These drugs have been shown to not only improve glycemic control but also provide additional benefits, such as weight loss and reduced risk of cardiovascular events.
Traditionally, the management of diabetes has relied on a combination of lifestyle modifications, oral antidiabetic medications, and insulin therapy. However, the introduction of SGLT2 inhibitors has opened up new possibilities for more comprehensive and personalized treatment approaches.
"SGLT2 inhibitors have the potential to become a cornerstone of combination therapy in diabetes management," says Dr. Emily Yates, an endocrinologist at a leading research hospital. "By targeting different mechanisms of action, these drugs can work synergistically with other antidiabetic medications to provide better glycemic control and improved overall outcomes for patients."
One of the key advantages of using SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy is their ability to address multiple aspects of diabetes management. When combined with metformin, the first-line medication for type 2 diabetes, SGLT2 inhibitors have been shown to enhance glycemic control, promote weight loss, and potentially reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and kidney disease.
Furthermore, SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy when used in combination with DPP-4 inhibitors, another class of oral antidiabetic medications. This combination can provide a comprehensive approach to managing hyperglycemia, as the two drug classes work through different mechanisms to regulate blood glucose levels.
"The synergistic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and DPP-4 inhibitors can be particularly beneficial for patients who struggle to achieve their target HbA1c levels with either medication alone," explains Dr. Yates. "By addressing multiple pathways involved in glucose homeostasis, this combination can lead to improved glycemic control and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications."
As the research on SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy continues to evolve, healthcare professionals are also exploring their potential role in the management of type 1 diabetes. While these drugs are primarily approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, some studies have suggested that they may also be beneficial for individuals with type 1 diabetes, particularly in addressing the challenge of glycemic variability and reducing the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.
"The use of SGLT2 inhibitors in type 1 diabetes is an emerging area of interest," says Dr. Yates. "While more research is needed, the initial findings indicate that these medications may have a place in the management of this condition, potentially in combination with insulin therapy."
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy for diabetes management is likely to become increasingly important. Healthcare professionals and researchers will need to carefully evaluate the evidence and tailor treatment approaches to meet the individual needs of each patient.
So, what's the future of SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy for diabetes? As with any emerging treatment approach, only time and ongoing research will tell. But one thing is certain: the potential benefits of this combination therapy are certainly worth exploring further.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
Is Combining Insulin with Oral Medications Effective for Diabetes Management?
Delve into the benefits and challenges of using a combination of insulin and oral medications for diabetes.
Exploring the Role of Metformin in Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Investigate the impact of metformin when used in combination therapy for diabetes management.
Are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists A Game-Changer in Combination Therapy for Diabetes?
Discuss the effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists as part of combination therapy for diabetes.
Combination Therapy: Balancing Insulin and Sulfonylureas for Diabetes Control
Balance the use of insulin and sulfonylureas in combination therapy for optimal diabetes control.
Combining DPP-4 Inhibitors with Other Medications for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Gain insights into the benefits and considerations of using DPP-4 inhibitors in combination therapy for diabetes.
Mixing Biguanides with Other Medications: Exploring Combination Therapy for Diabetes
Examine the implications of combining biguanides with other medications for diabetes treatment.
Beyond Monotherapy: The Impact of Combination Therapy in Diabetes Care
Dive into the significance of transitioning from monotherapy to combination therapy in diabetes care.
Combination Therapy: Harnessing the Power of Multiple Agents for Diabetes Control
Uncover the synergistic effects of utilizing multiple agents in combination therapy for diabetes control.
Patient Perspectives on Combination Therapy: Shaping Diabetes Treatment Strategies
Explore the patient-centric approach to integrating combination therapy into diabetes treatment strategies.